Nanoparticles play a transformative role in pulmonary drug delivery systems (PDDS) by enhancing drug bioavailability, targeting and controlled release in the lungs. These nano-sized carriers, such as liposomes, polymeric nanoparticles and solid lipid nanoparticles, provide improved solubility for hydrophobic drugs and reduce systemic side effects. Their small size allows deep penetration into alveolar regions, enabling local treatment of respiratory diseases such as asthma, COPD and lung cancer. Functional nanoparticles can further achieve site-specific delivery through surface modifications. They are ideal for both small molecules and biologics such as peptides and siRNA, making PDDS a leader in precision pulmonary therapeutics.
Introduction on Pulmonary Drug Delivery Systems
Pulmonary drug delivery system (PDDS) refers to the direct administration of therapeutic agents to the lungs through the respiratory system, offering a highly effective method for treating a variety of pulmonary conditions.
This approach is particularly beneficial for diseases such as:
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Pulmonary infections, and even lung cancer
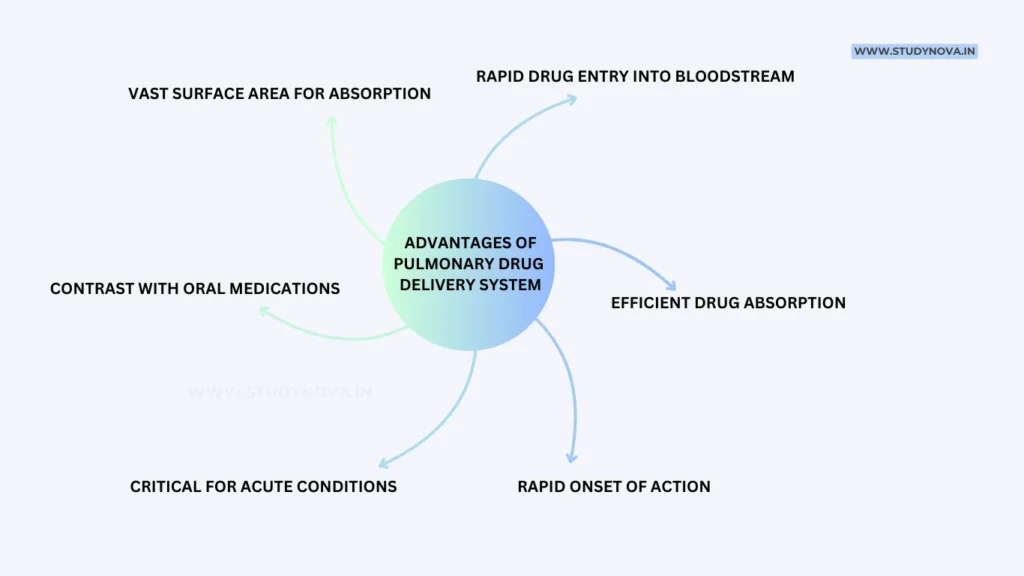
Advantages of pulmonary drug delivery (PDD):
- Vast surface area for absorption: The lungs contain millions of tiny alveoli, providing an enormous absorptive surface for quick drug uptake.
- Rapid drug entry into bloodstream: Drugs can quickly reach the bloodstream and exert therapeutic effects, especially when the primary site of disease is the respiratory tract.
- Efficient drug absorption: PDDS (Pulmonary Drug Delivery System) allows drugs to be absorbed quickly through the lungs.
- Rapid onset of action: Direct delivery to the lungs enables immediate access to the target site.
- Critical for acute conditions: Essential for treating fast-acting conditions like asthma attacks or respiratory infections.
- Contrast with oral medications: Oral drugs must be digested, absorbed, and metabolized by the liver, delaying therapeutic effects.
- Bypasses the gastrointestinal (GI) tract: Pulmonary drug delivery system (PDDS) avoids the GI tract entirely, reducing the risk of systemic side effects typically seen with oral medications. Especially beneficial for drugs that cause GI irritation, liver strain, or other adverse effects when taken orally.
- Smaller doses, effective treatment: Pulmonary drug delivery system (PDDS) allows for drug delivery in smaller doses while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. Localized delivery to the lungs ensures the drug is concentrated where it is needed, reducing the amount required.
- Minimizes systemic side effects: The targeted approach reduces the risk of systemic side effects by focusing the drug’s action on the lungs.
- Precision targeting: Direct lung delivery ensures the drug reaches the intended site of action with high precision, enhancing treatment efficacy.
- Particularly useful for lung diseases: For diseases like lung cancer, Pulmonary drug delivery system (PDDS) enables targeted delivery to tumor cells, improving treatment efficacy while minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
- Promising approach for lung-related diseases: Pulmonary drug delivery system (PDDS) offers a combination of efficiency, speed, and precision that is increasingly being utilized for treating lung conditions.
Nanoparticles (NPs) in pulmonary drug delivery system:
Size and surface area of NPs are small (1 to 100 nm) with a large surface area relative to their volume, making them efficient for lung tissue interaction. Their small size allows NPs to reach deep areas of the lungs, including the alveoli, which are difficult to target with conventional methods. Nanoparticles provide a precise and efficient method for drug delivery to the lungs, allowing for targeted treatment of specific cells or tissues, such as inflamed areas or tumor cells.
Surface modifications, like coating with targeting ligands, enable nanoparticles to be directed to the exact site needed, enhancing drug effectiveness and minimizing exposure to healthy tissue.
Advantages for lung diseases:
- NPs are ideal for treating respiratory conditions like asthma, COPD, and pulmonary infections by targeting the deeper lung regions.
Customization for specific therapeutic purposes:
- NPs can be engineered to carry various drugs (small molecules or biologics) and release them in a controlled, targeted manner.
- They can protect drugs from degradation and ensure precise delivery to the lungs.
Controlled and sustained release:
- Nanoparticles can be designed for sustained or prolonged drug release over time, improving treatment for chronic conditions.
- This approach is beneficial for diseases like COPD, where long-term drug delivery with fewer doses enhances patient compliance and treatment effectiveness.
The controlled release properties of nanoparticles ensure drugs stay active for longer periods at the right concentration, improving treatment outcomes. Nanoparticles reduce the required drug dose, improve drug bioavailability in the lungs, and lower the risk of systemic side effects. These formulations can be administered via inhalers or nebulizers, offering a non-invasive, patient-friendly route of delivery.
As research advances, nanoparticles in pulmonary drug delivery show great potential for treating a wide range of lung diseases with greater precision, efficacy, and improved patient compliance.